ADHD: Should You See a Neurologist or Psychiatrist?
At Diligence Integrated Care, we often hear patients ask whether they should see an ADHD neurologist vs psychiatrist for their attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. This question highlights the complexity of ADHD treatment and the importance of choosing the right specialist.
In this post, we’ll explore the roles of neurologists and psychiatrists in ADHD care, helping you make an informed decision about your treatment path.
What Is ADHD and How Does It Affect Daily Life?
Understanding ADHD: A Complex Neurodevelopmental Condition
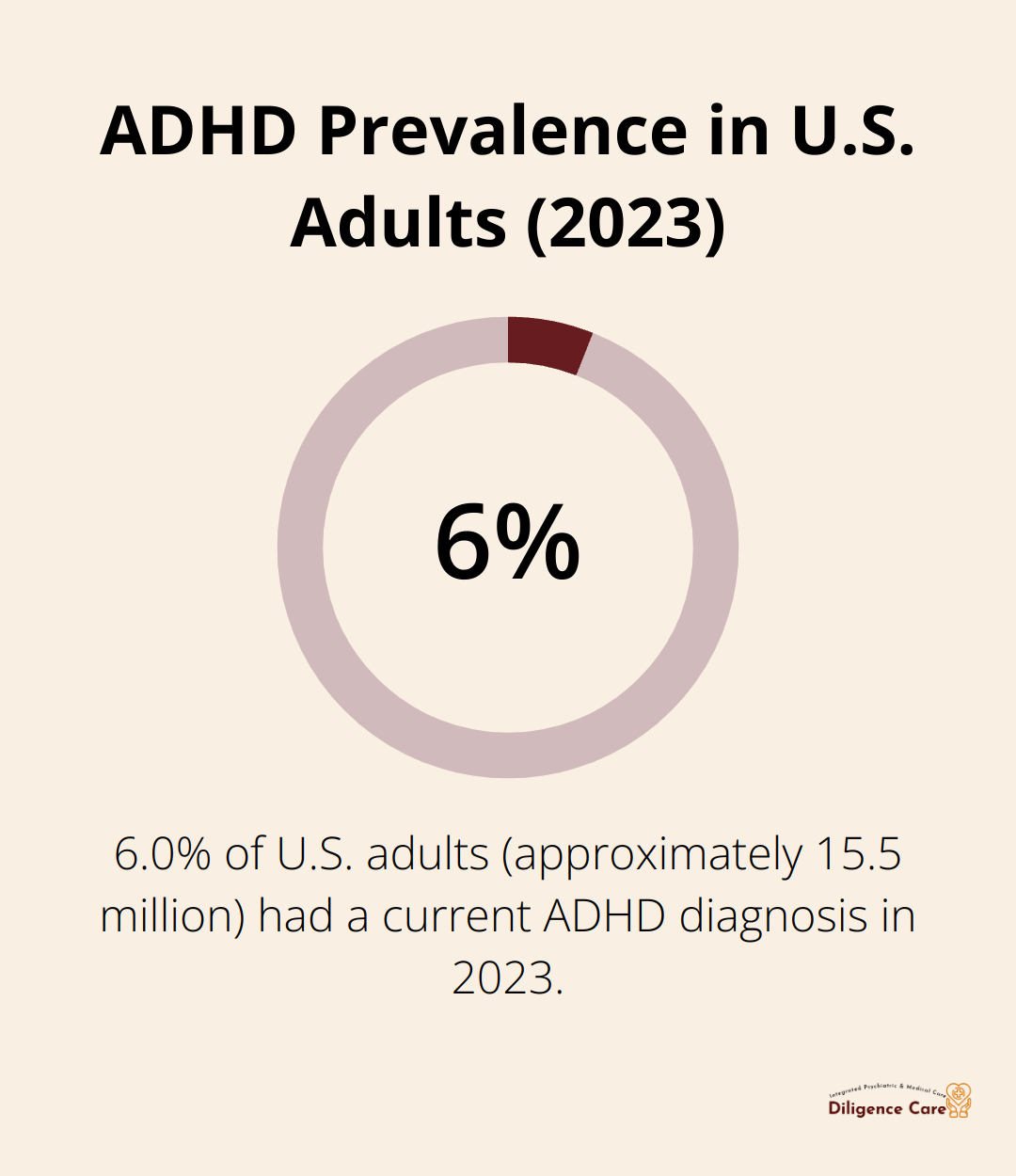
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that impacts millions of adults and children worldwide. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that approximately 15.5 million U.S. adults (6.0%) had a current ADHD diagnosis in 2023. This disorder manifests through persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning and development.
The Diverse Manifestations of ADHD
ADHD presents differently in each individual. Some people primarily struggle with inattention, finding it challenging to focus on tasks, follow instructions, or complete work. Others experience hyperactivity and impulsivity, feeling restless, interrupting conversations, or making hasty decisions. Many individuals exhibit a combination of these symptoms.
ADHD’s Profound Impact on Daily Life
The effects of ADHD extend far beyond occasional forgetfulness or fidgeting. Adults with ADHD often face significant challenges in their personal and professional lives. They may struggle with time management (leading to missed deadlines or appointments), experience relationship difficulties due to perceived inattentiveness or impulsive behavior, and encounter work-related issues such as difficulty organizing tasks, following through on projects, or maintaining focus during meetings.
The Critical Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective ADHD management. Unfortunately, many adults remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for years. A study found that of 134 adults with ADHD, 56 (42%) were diagnosed in childhood (<18 years of age) and 78 (58%) were diagnosed in adulthood (≥18 years of age). Misdiagnosis is also common, with many adults undergoing multiple misdiagnoses and consulting an average of 2.3 doctors before receiving the correct diagnosis.
Treatment: A Comprehensive Approach
Effective ADHD treatment typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Doctors often prescribe stimulant medications like amphetamine (Adderall) and methylphenidate (Ritalin) to increase dopamine levels and improve focus. However, medication alone is often insufficient. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help adults with ADHD develop coping strategies, improve time management skills, and address negative thought patterns.
The complexity of ADHD necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment. While neurologists focus on the biological aspects of the disorder, psychiatrists offer a more holistic perspective that addresses behavioral, psychological, and emotional factors. In the next section, we will explore the specific roles of neurologists and psychiatrists in ADHD care, helping you make an informed decision about your treatment path.
Neurologists and ADHD: A Brain-Focused Approach
Neurologists offer a unique perspective on ADHD, focusing on the disorder’s biological aspects. Their expertise in brain structure and function provides valuable insights into this complex condition.
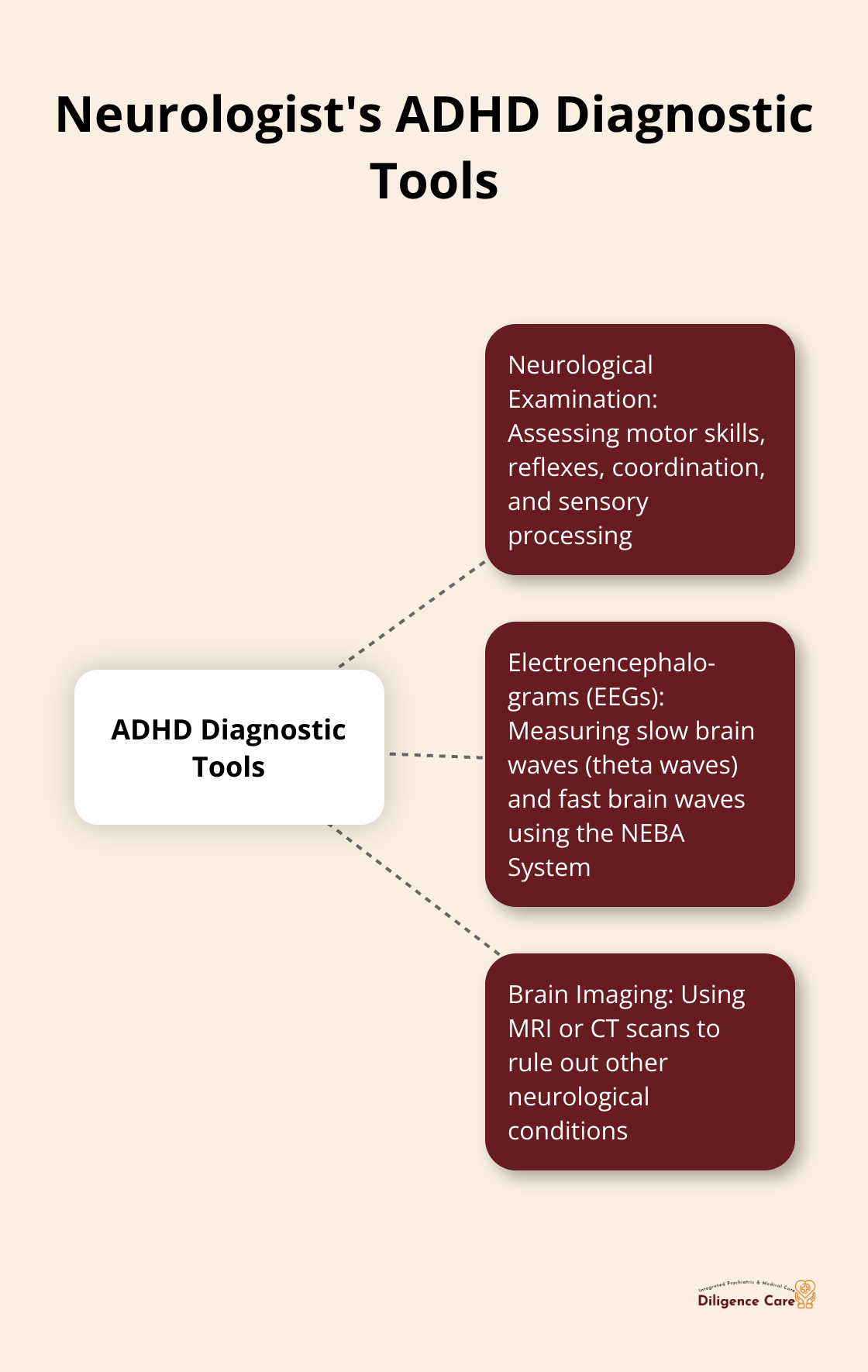
Diagnostic Tools Used by Neurologists
Neurologists employ various tools to assess ADHD:
- Neurological Examination: Assessing motor skills, reflexes, coordination, and sensory processing.
- Electroencephalograms (EEGs): The Neuropsychiatric EEG-Based Assessment Aid (NEBA) System measures slow brain waves called theta waves and fast brain waves.
- Brain imaging: MRI or CT scans help rule out other neurological conditions.
While not always necessary for an ADHD diagnosis, these tests prove helpful in complex cases or when other neurological conditions are suspected.
When to Consult a Neurologist for ADHD
Consider seeing a neurologist for ADHD if you:
- Have a history of head injuries or other neurological conditions
- Experience atypical or severe symptoms
- Haven’t responded well to standard ADHD treatments
- Face cognitive difficulties beyond typical ADHD symptoms
Dr. Bolanle Oluwadara, MD, at Diligence Integrated Care specializes in neurological aspects of ADHD. Her expertise proves particularly valuable for patients with complex presentations or those who haven’t found success with traditional treatments.
The Neurologist’s Contribution to ADHD Management
Once diagnosed, a neurologist contributes to your ADHD management plan in several ways:
- Prescribing and monitoring medication
- Recommending lifestyle changes to support brain health
- Addressing any co-existing neurological conditions
It’s important to note that while neurologists offer valuable insights, they may not provide the comprehensive psychological support that many ADHD patients need. A combined approach, leveraging the expertise of both neurologists and psychiatrists, often yields the most effective care.
The Limitations of a Purely Neurological Approach
While neurologists excel at understanding the brain’s physical aspects, ADHD management often requires a more holistic approach. Psychological and emotional factors play a significant role in ADHD symptoms and treatment outcomes. This is where psychiatrists come into play, offering a complementary perspective that addresses the full spectrum of ADHD-related challenges.
As we transition to discussing the role of psychiatrists in ADHD management, it’s clear that both specialties bring unique strengths to the table. The next section will explore how psychiatrists approach ADHD treatment and how their methods differ from (and complement) those of neurologists.
How Psychiatrists Approach ADHD Treatment
Comprehensive Evaluation and Diagnosis
Psychiatrists conduct thorough evaluations to diagnose ADHD accurately. This process typically involves:
- Detailed patient history
- Behavioral assessments
- Psychological testing
- Ruling out other mental health conditions
A recent study validated the diagnostic accuracy of an online ADHD assessment among individuals seeking online behavioral healthcare, demonstrating the potential for comprehensive evaluations to lead to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment outcomes.
Personalized Medication Management
Medication often forms a key component of ADHD treatment. Psychiatrists prescribe and manage ADHD medications, including stimulants and non-stimulants. They consider factors such as:
- Symptom severity
- Co-existing conditions
- Potential side effects
- Patient preferences
A recent survey by the American Psychiatric Association revealed that 85% of adults with ADHD who received medication management from a psychiatrist reported improved focus and productivity at work.

Integrating Therapy and Behavioral Interventions
Psychiatrists recognize that a multi-modal approach often yields the best results. They frequently incorporate various therapeutic techniques into treatment plans, such as:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Mindfulness-based interventions
- Social skills training
- Executive function coaching
Recent research has shown that conventional pharmacological interventions have proven their efficacy in alleviating core ADHD symptoms in adults, providing rapid relief.
Addressing Co-occurring Conditions
Many individuals with ADHD also experience co-occurring mental health conditions. Psychiatrists assess and treat these conditions alongside ADHD. Common co-occurring conditions include:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Substance use disorders
- Learning disabilities
A comprehensive approach to these co-occurring conditions often improves overall treatment outcomes.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment
ADHD treatment requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Psychiatrists schedule regular follow-up appointments to:
- Assess treatment effectiveness
- Adjust medication dosages if necessary
- Address any side effects
- Modify therapeutic interventions as needed
This continuous care ensures that the treatment plan evolves with the patient’s changing needs and circumstances.
Final Thoughts
The choice between an ADHD neurologist and psychiatrist depends on your specific needs. Neurologists focus on biological aspects, while psychiatrists offer a more comprehensive approach. At Diligence Integrated Care, we believe in integrated care that addresses all aspects of ADHD.
Our team of specialists works together to create personalized treatment plans. We tailor our approach to your specific symptoms and life circumstances. Our comprehensive ADHD testing and treatment services provide the support you need to thrive.
If you struggle with ADHD symptoms, professional support can make a difference. At Diligence Integrated Care, we help you navigate your ADHD journey with compassion and expertise. Your path to better mental health starts with us.











